Aerothermia : ¿ What is and how works ?
In the realm of energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions, aerothermia has emerged as a promising technology. As sustainability becomes a key focus in the construction and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) industries, aerothermia presents an innovative approach to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions. This article will delve into the concept of aerothermia, explaining what it is and how it works, while highlighting its benefits and applications.
Aerothermy
In the realm of energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions, aerothermia has emerged as a promising technology. As sustainability becomes a key focus in the construction and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) industries, aerothermia presents an innovative approach to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions. This article will delve into the concept of aerothermia, explaining what it is and how it works, while highlighting its benefits and applications.
What is Aerothermia?
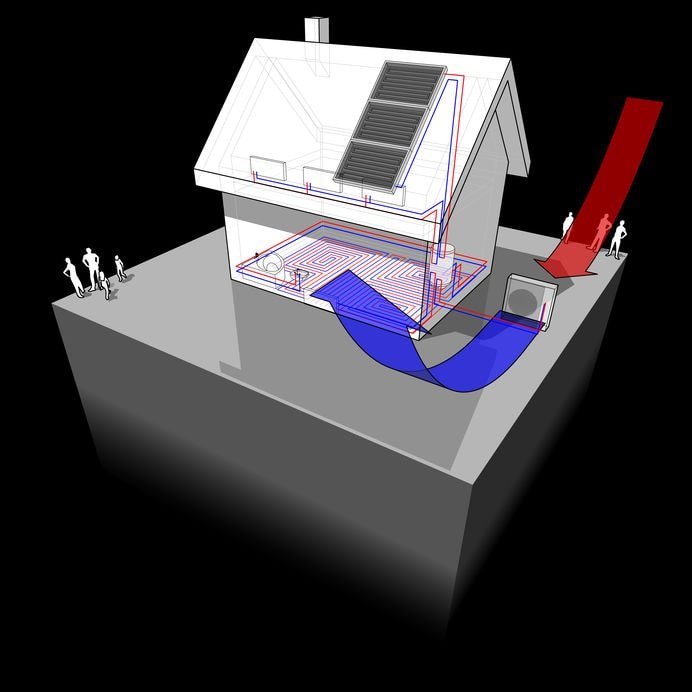
Aerothermia, also known as air source heat pumps, is a heating and cooling system that utilizes the energy present in the ambient air to regulate indoor temperatures. It harnesses the renewable energy available in the atmosphere, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional heating and cooling methods that heavily rely on fossil fuels. By extracting heat from the air during colder periods and dissipating heat during warmer periods, aerothermia offers a year-round solution for maintaining comfortable indoor climates.
How Does Aerothermia Work?
The Operating Principle of Aerothermia
Aerothermia systems function based on the principle of heat exchange. The process begins with an outdoor unit containing a fan, a refrigerant circuit, and a compressor. The fan draws in ambient air, which passes through the evaporator, where a refrigerant with a low boiling point circulates. As the air comes into contact with the cold evaporator, heat energy is transferred from the air to the refrigerant, causing the refrigerant to evaporate.
The Heat Pump Cycle
Once the refrigerant vaporizes, it flows into the compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. The heated refrigerant then passes through a condenser, releasing the collected heat energy into the indoor space. This transfer of heat raises the temperature of the circulated air, which is then distributed throughout the building via a network of ducts or pipes.
Reversible Operation for Cooling
A unique advantage of aerothermia systems is their ability to operate in reverse mode during warmer seasons, providing cooling capabilities. By reversing the refrigerant flow, the heat pump can extract heat from the indoor air and release it outdoors. This process effectively cools the indoor environment, allowing users to maintain comfortable temperatures year-round without the need for separate cooling systems.
Benefits and Applications of Aerothermia
Aerothermia systems offer several advantages, making them a popular choice for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Some key benefits include:
- Energy Efficiency: Aerothermia systems can provide substantial energy savings compared to traditional heating and cooling methods. By harnessing the renewable energy from the air, they can deliver efficient heating and cooling with reduced environmental impact.
- Cost Savings: Lower energy consumption translates into reduced utility bills, making aerothermia an economically viable option in the long run. Additionally, in some regions, incentives and subsidies may be available to further offset installation costs.
- Environmental Friendliness: By utilizing renewable energy, aerothermia significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to a greener future. It helps combat climate change and promotes sustainability.
- Versatility: Aerothermia systems can be used for both heating and cooling purposes, providing a versatile solution for year-round temperature control.
How does air to air heating work?
Air-to-air heating refers to a type of heating system that uses outdoor air as a heat source to warm indoor spaces. The process typically involves the use of an air-source heat pump, which extracts heat from the outdoor air and transfers it inside.
Here’s a simplified explanation of how air-to-air heating works:
- Outdoor Unit: The air-to-air heating system consists of an outdoor unit, which contains a fan, a compressor, a heat exchanger, and refrigerant coils. The unit is usually placed outside the building.
- Heat Extraction: The fan in the outdoor unit pulls in outdoor air, which passes over the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger contains a refrigerant fluid that evaporates at a low temperature, absorbing heat from the outdoor air.
- Refrigerant Circulation: The compressor in the outdoor unit compresses the refrigerant, increasing its temperature and pressure. This compressed, high-temperature refrigerant then moves to the indoor unit through refrigerant lines.
- Indoor Unit: Inside the building, the indoor unit, typically located in the utility room or basement, contains a heat exchanger, a fan, and a control system.
- Heat Distribution: The high-temperature refrigerant flows through the indoor unit’s heat exchanger, transferring its heat to the indoor air. The fan blows over the heat exchanger, distributing the warm air throughout the building via ductwork and vents.
- Heat Release: As the refrigerant releases its heat to the indoor air, it cools down and becomes a low-pressure gas again.
- Refrigerant Return: The cooled refrigerant returns to the outdoor unit through the refrigerant lines, and the cycle repeats.
The air-to-air heating system can also function as an air conditioner during warmer months. In this case, the system reverses the refrigerant flow, extracting heat from indoor air and releasing it outside, effectively cooling the indoor space.
It’s important to note that air-to-air heating systems are most efficient in moderate climates. In extremely cold temperatures, they may need additional heating support or backup systems to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
In conclusion, aerothermia is a cutting-edge technology that harnesses the renewable energy present in the ambient air to regulate indoor temperatures efficiently. With its energy-saving potential, cost-effectiveness, and positive environmental impact, aerothermia is rapidly gaining popularity across various sectors. By opting for this sustainable heating and cooling solution, individuals and businesses can contribute to a greener future while enjoying optimal comfort throughout the year.






